 |
| Factor Affecting Seed Germination. https://cststudy.blogspot.com/ |
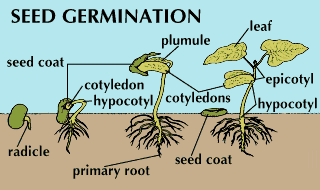
Factor Affecting Seed Germination
1.Water is required for germination. Mature and roller
coaster seeds are often extremely dry and need to take in significant amounts
of water, relative to the dry weight of the seed, before cellular metabolism
and growth can resume. Most seeds need enough water to moisten the seeds but
not enough to soak them.
The uptake of water by seeds is called imbibition, which leads to the swelling and the breaking of the seed coat. When seeds are formed, most plants store a food reserve with the seed, such as starch, proteins, or oils. This food reserve provides nourishment to the growing embryo.
When the seed imbibes water, hydrolytic enzymes are activated which break down these stored food resources into metabolically useful chemicals. After the seedling emerges from the seed coat and starts growing roots and leaves, the seedling's food reserves are typically exhausted; at this point photosynthesis provides the energy needed for continued growth and the seedling now requires a continuous supply of water, nutrients, and light.
The uptake of water by seeds is called imbibition, which leads to the swelling and the breaking of the seed coat. When seeds are formed, most plants store a food reserve with the seed, such as starch, proteins, or oils. This food reserve provides nourishment to the growing embryo.
When the seed imbibes water, hydrolytic enzymes are activated which break down these stored food resources into metabolically useful chemicals. After the seedling emerges from the seed coat and starts growing roots and leaves, the seedling's food reserves are typically exhausted; at this point photosynthesis provides the energy needed for continued growth and the seedling now requires a continuous supply of water, nutrients, and light.
2.Oxygen is required by the germinating seed for metabolism.
Oxygen is used in aerobic respiration, the main source of the seedling's energy
until it grows leaves. Oxygen is an atmospheric gas that is found in
soil pore spaces; if a seed is buried too deeply within the soil or the soil is
waterlogged, the seed can be oxygen starved.
Some seeds have impermeable seed coats that prevent oxygen from entering the seed, causing a type of physical dormancy which is broken when the seed coat is worn away enough to allow gas exchange and water uptake from the environment.
Some seeds have impermeable seed coats that prevent oxygen from entering the seed, causing a type of physical dormancy which is broken when the seed coat is worn away enough to allow gas exchange and water uptake from the environment.
3.Temperature affects cellular metabolic and growth rates. Seeds
from different species and even seeds from the same plant germinate over a wide
range of temperatures. Seeds often have a temperature range within which they
will germinate, and they will not do so above or below this range.
Many seeds germinate at temperatures slightly above 60-75 F (16-24 C) [room-temperature if you live in a centrally heated house], while others germinate just above freezing and others germinate only in response to alternations in temperature between warm and cool. Some seeds germinate when the soil is cool 28-40 F (-2 - 4 C), and some when the soil is warm 76-90 F (24-32 C). Some seeds require exposure to cold temperatures (vernalization) to break dormancy. Some seeds in a dormant state will not germinate even if conditions are favorable.
Seeds that are dependent on temperature to end dormancy have a type of physiological dormancy. For example, seeds requiring the cold of winter are inhibited from germinating until they take in water in the fall and experience cooler temperatures. Four degrees Celsius is cool enough to end dormancy for most cool dormant seeds, but some groups, especially within the family Ranunculaceae and others, need conditions cooler than -5 C. Some seeds will only germinate after hot temperatures during a forest fire which cracks their seed coats; this is a type of physical dormancy.
Many seeds germinate at temperatures slightly above 60-75 F (16-24 C) [room-temperature if you live in a centrally heated house], while others germinate just above freezing and others germinate only in response to alternations in temperature between warm and cool. Some seeds germinate when the soil is cool 28-40 F (-2 - 4 C), and some when the soil is warm 76-90 F (24-32 C). Some seeds require exposure to cold temperatures (vernalization) to break dormancy. Some seeds in a dormant state will not germinate even if conditions are favorable.
Seeds that are dependent on temperature to end dormancy have a type of physiological dormancy. For example, seeds requiring the cold of winter are inhibited from germinating until they take in water in the fall and experience cooler temperatures. Four degrees Celsius is cool enough to end dormancy for most cool dormant seeds, but some groups, especially within the family Ranunculaceae and others, need conditions cooler than -5 C. Some seeds will only germinate after hot temperatures during a forest fire which cracks their seed coats; this is a type of physical dormancy.
Most common annual
vegetables have optimal germination temperatures between 75-90 F (24-32 C),
though many species (e.g. radishes or spinach) can germinate at significantly
lower temperatures, as low as 40 F (4 C), thus allowing them to be grown from
seeds in cooler climates. Suboptimal temperatures lead to lower success rates
and longer germination periods.
4.Light or darkness can be an environmental trigger for germination and
is a type of physiological dormancy. Most seeds are not affected by light or
darkness, but many seeds, including species found in forest settings, will not
germinate until an opening in the canopy allows sufficient light for growth of
the seedling.
Scarification
mimics natural processes that weaken the seed coat before germination. In
nature, some seeds require particular conditions to germinate, such as the heat
of a fire (e.g., many Australian native plants), or soaking in a body of water
for a long period of time. Others need to be passed through an animal's
digestive tract to weaken the seed coat enough to allow the seedling to emerge.
Comments
Post a Comment